- Real-time object detection using OpenCV in Python.
- Face recognition algorithm
- First, look at a picture and find all the faces in it
- Second, focus on each face and be able to understand that even if a face is turned in a weird direction or in bad lighting, it is still the same person.
- Third, be able to pick out unique features of the face that you can use to tell it apart from other people— like how big the eyes are, how long the face is, etc.
- Finally, compare the unique features of that face to all the people you already know to determine the person’s name.

Object recognition algorithm:
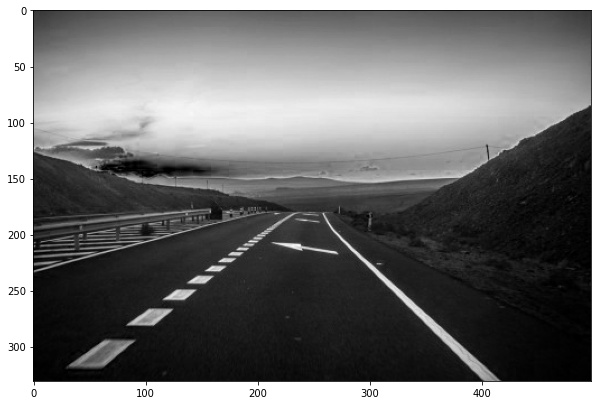
- Importing image
- converting into numpy arrays
- Processing the image to greyscale
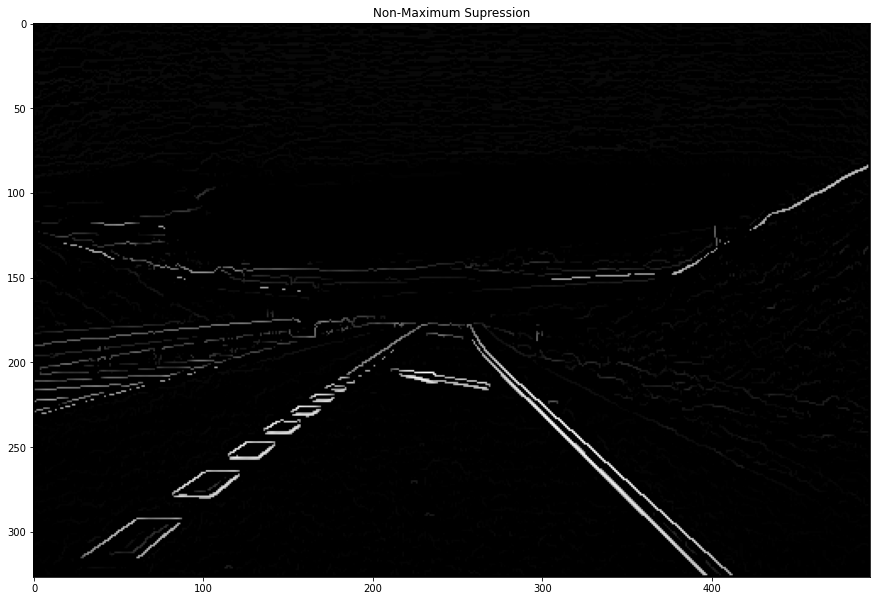
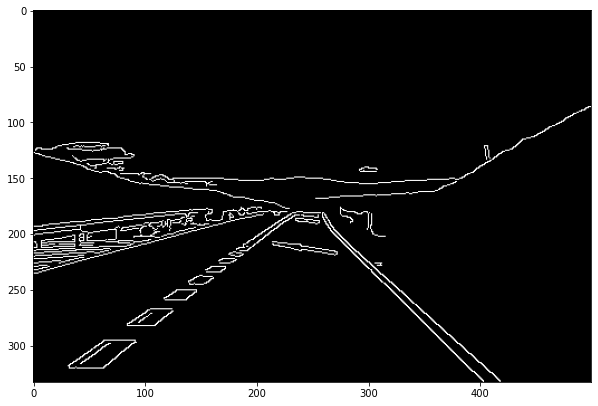
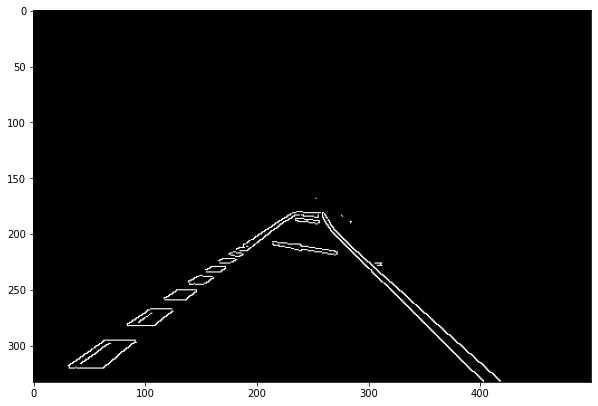
- Canny Edge Detection
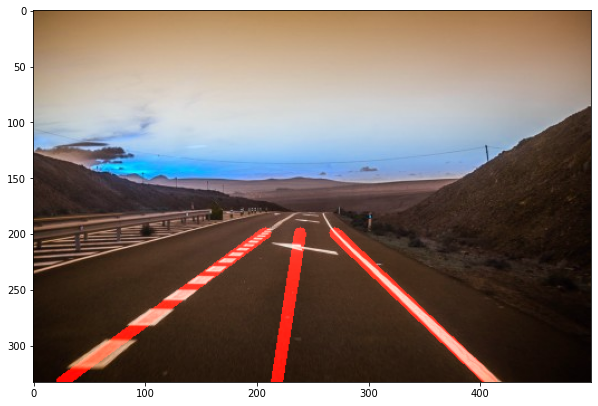
- Lane detection




Pseudo Code
import requests
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def get_image_from_url(url, im_name):
try:
img_resp = requests.get(url , timeout = 1)
fh = open( im_name , 'wb')
fh.write( img_resp.content )
except:
print('Error while getting the image')
return Image.open( im_name )
def show_img(im,gray=False):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10,10))
if gray:
ax.imshow(im,cmap='gray')
else:
ax.imshow(im)
im = get_image_from_url('https://www.ticketsnipers.com/assets/traffic_ticket/_small_citation_photo/CVC_21460.5.jpg','test_img.png')
im
# converting image into numpy arrays
np_im = np.array(im)
print('PIL Image format WxH: {}'.format(im.size))
print('NumPy Image format HxWxC: {}'.format(np_im.shape))
# greyscale conversion
np_im[:,0:10,:] = 0;
im_processed = Image.fromarray(np_im, 'RGB')
im_processed.save('test_img_proc.png')
im_processed
np_im = np.array(im)
np_im_gray = np_im.min(axis=2)
show_img(np_im_gray,True)
# canny edge detection
def non_max_suppression(img, D):
M, N = img.shape
Z = np.zeros((M,N), dtype=np.int32)
# Transform radians to degrees for easier processing
# The output value will be [-pi,pi]
angle = D * 180. / np.pi
angle = angle%360
#reflect over the x axis
angle[angle < 0] += 180
for i in range(1,M-1):
for j in range(1,N-1):
try:
a = img[i,j]
b = 255.0
c = 255.0
#angle 0
if (0 <= angle[i,j] < 22.5) or (157.5 <= angle[i,j] <= 180):
b = img[i, j+1]
c = img[i, j-1]
#angle 45
elif (22.5 <= angle[i,j] < 67.5):
b = img[i+1, j-1]
c = img[i-1, j+1]
#angle 90
elif (67.5 <= angle[i,j] < 112.5):
b = img[i+1, j]
c = img[i-1, j]
#angle 135
elif (112.5 <= angle[i,j] < 157.5):
b = img[i-1, j-1]
c = img[i+1, j+1]
if (a >= b) and (a >= c):
Z[i,j] = a
else:
Z[i,j] = 0
except IndexError as e:
print('Error Found')
return Z
def canny(image):
gray = cv2.cvtColor(lane_image, cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY) # convert to grayscale
blur = cv2.GaussianBlur(gray,(5,5),0) # reduce noise
canny = cv2.Canny(blur,50,150) # Find the edges
return gray,blur,canny
def region_of_interest(image):
height,width = image.shape[0],image.shape[1]
polygons = np.array([[(0,height),(width,height),(int(width/2),int(0.5*height))]])
mask = np.zeros_like(image) # black
cv2.fillPoly(mask,polygons,255) # white
maskded_image = cv2.bitwise_and(image,mask)
return mask,maskded_image
def display_line(image,lines):
line_image = np.zeros_like(image)
height, width, channels = image.shape
if lines is not None:
for x1, y1, x2, y2 in lines:
cv2.line(line_image,(int(x1), int(y1)),(int(x2), int(y2)),(255, 0, 0), 10)#only one line
print("width:%s,height:%s,channels:%s" % (width, height, channels))
#cv2.line(line_image, (int(width/2), int(height)), (int(width/2), int(height*0.6)), (0, 255, 0), 10) # only one line
return line_image
def make_coordinate(image,line_parameters):
slope, intercept = line_parameters
y1 = image.shape[0]
y2 = int(y1*3/5)
x1 = int((y1-intercept)/slope)
x2 = int((y2-intercept)/slope)
return np.array([x1, y1, x2, y2])
#-------------------average------------
def average_slope_intercept(image,lines):
left_fit = []
right_fit = []
for line in lines:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = line.reshape(4)
parameters = np.polyfit((x1, x2),(y1, y2),1)
#print(parameters)
slope = parameters[0]
intercept = parameters[1]
if slope<0:
left_fit.append((slope,intercept))
else:
right_fit.append((slope,intercept))
left_fit_average = np.average(left_fit, axis = 0)
right_fit_average = np.average(right_fit, axis = 0)
left_line = make_coordinate(image,left_fit_average)
right_line = make_coordinate(image,right_fit_average)
mid_line = (left_line+right_line)/2
return np.array([left_line,right_line,mid_line])